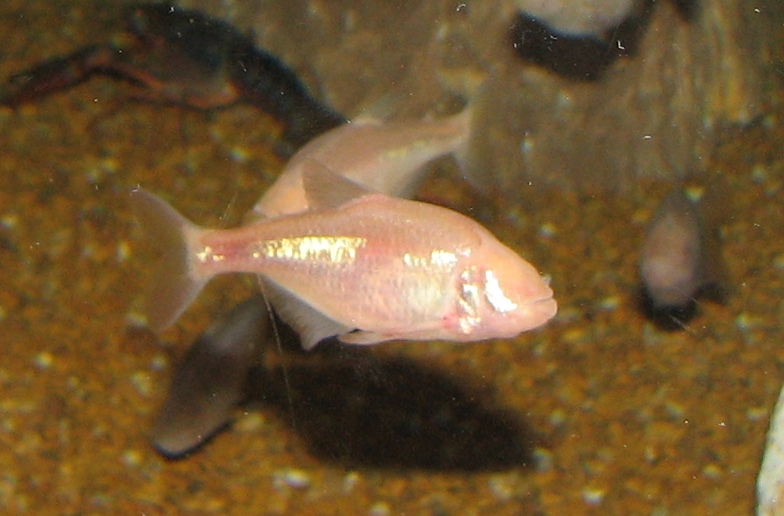
Yes, you read that right, Mexican Tetra fish (Astyanax mexicanus) are blind! Their eyes have regressed over time, leaving them with only a few remaining photoreceptor cells that can detect light and dark.
Instead, they rely on other senses, such as their lateral line system, which helps them detect vibrations in the water, and their sense of smell, which helps them find food.
But how do these fish survive in such harsh conditions? Well, they have evolved some pretty remarkable traits.
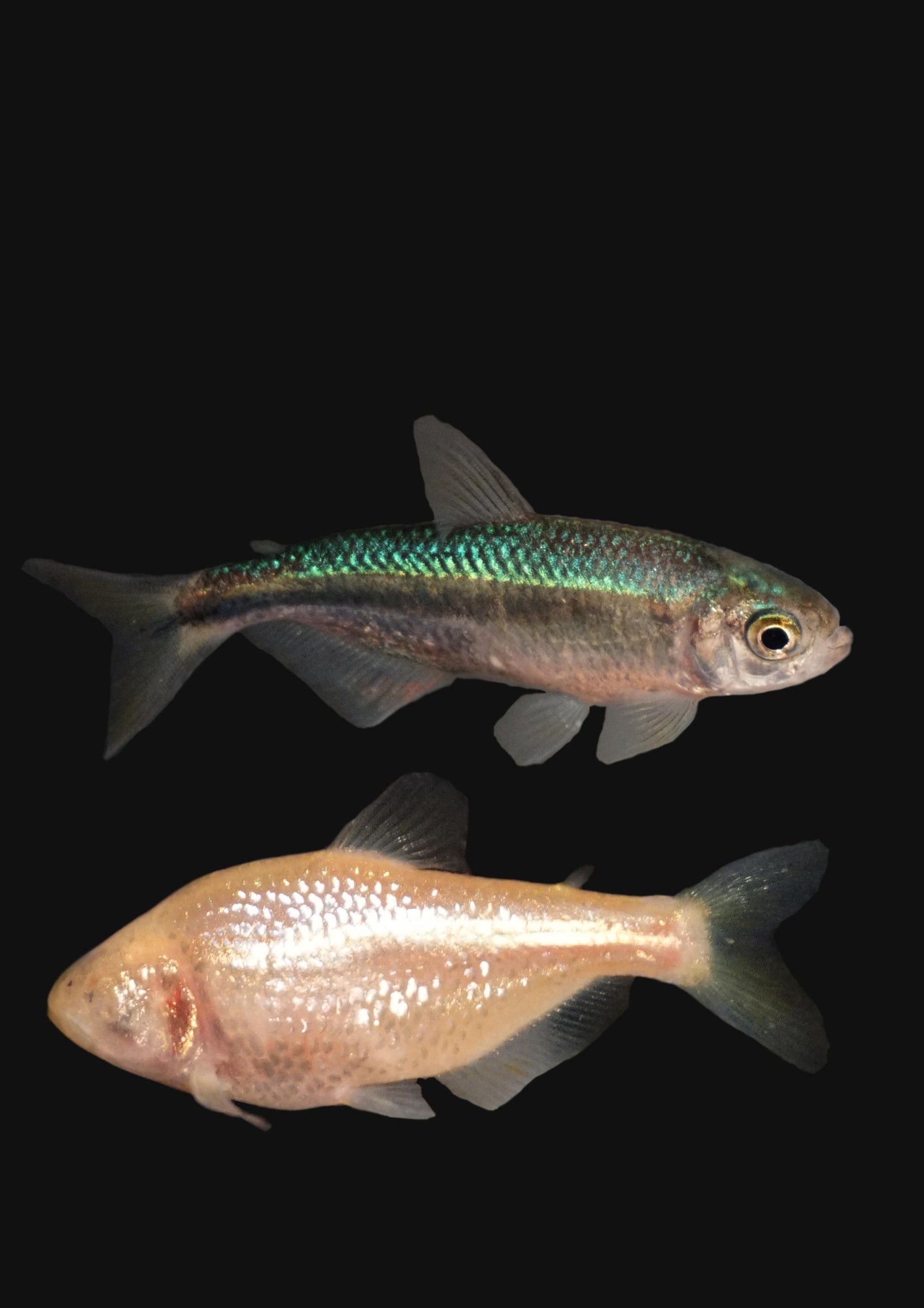
One of the most notable adaptations is their ability to switch between two forms: surface-dwelling and cave-dwelling. Surface-dwelling fish have eyes and are pigmented, while cave-dwelling fish are eyeless and have no color.
This switch in form is controlled by a single gene and is triggered by environmental cues, such as light and food availability.
Mexican tetra fish have also developed a unique feeding behavior.
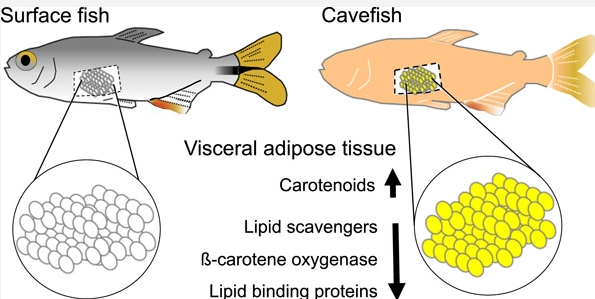
In caves, where food is scarce, they have evolved to feed on bat guano, which falls into the water from the bats that roost in the caves.
They have developed a specialized mouth shape that allows them to scrape the guano off the cave walls and filter out the nutrients.
Despite living in such extreme conditions, Mexican tetra fish play an important ecological role.
They are a keystone species in the underground cave ecosystem, serving as a food source for larger cave-dwelling animals, such as blind salamanders and crayfish.
They also help to cycle nutrients in the cave system, which supports the growth of microbial communities that are important for the cave ecosystem.
In this article, we will dive deeper into the world of Mexican tetra fish, exploring their fascinating adaptations, behavior, and ecological significance.
We will also discuss the threats they face, including habitat loss and pollution, and the efforts being made to conserve this unique species.
Join us on this journey to discover the wonders of the Mexican tetra fish, a true marvel of evolution.
Types of Mexican Tetra Fish
Normal Form (Surface-Dwelling Tetra)
The Mexican Tetra surface variety is a common characin species with a typical shape and silver scales. It can reach a maximum length of 12 cm (4.7 in).
In its natural habitat, Surface-Dwelling Mexican Tetra is known for its aggressive predatory behavior, often preying on other animals that inhabit the surface of the water.
However, when it is introduced into non-native environments, there is a growing concern that it may negatively impact local populations by targeting the young of native species.
On the positive side, this species is very social and tends to form large groups with clear hierarchies.
They also have a collective response to predators, which means that they work together to defend themselves against potential threats.
Overall, while the surface variety may have some negative impacts on local ecosystems, it also has some interesting social behaviors that are worth studying further.
Blind form (Blind Cave Tetra)
On the other hand, its blind cave form lacks eyes and pigmentation, and has a pinkish-white body color resembling an albino. It is known as the hypogean blind cave form and has been identified as a separate species, A. jordani, although this contradicts phylogenetic evidence.
The Blind Cave Tetra is a fascinating fish species that has evolved in a unique way due to its habitat.
Unlike its surface-dwelling twin, the blind cave form has lost its tendency to rely on group behavior for socialization and protection from predators.
Instead, it prefers to swim mostly alone, with just enough interaction with others of its kind for breeding purposes.
This solitary behavior is a result of its regressive traits, which have led to a more peaceful disposition than its surface-dwelling twin. However, this doesn’t mean that the Blind Cave Tetra is unfriendly or unapproachable.
They may be a bit shy at first, but after some time, they will memorize their surroundings and get around with ease.
When kept in an aquarium, Blind Cave Tetras prefer to swim in the middle region of the tank, and they will appreciate having plenty of hiding places to retreat to when they feel threatened.
Despite their lack of reliance on group behavior, they can still be kept with other fish species as long as they are peaceful and non-aggressive.
Lifespan and Life Cycle of Mexican Tetra Fish
If you are planning to keep these fish, it is important to understand their lifespan and life cycle.
Lifespan:
Mexican tetra fish have a relatively short lifespan, with an average of three to five years. However, with proper care and a healthy diet, they can live up to seven years. Factors that can affect their lifespan include water quality, diet, and genetics.
Breeding:
Mexican blind cave tetra fish reach sexual maturity at around one year of age. They breed throughout the year, with females producing up to 100 eggs per breeding cycle. To breed, it is recommended to keep a ratio of two females to one male in the aquarium.
Eggs:
The eggs of Mexican tetra fish hatch after two to three days, depending on water temperature. The fry, or baby fish, are tiny and vulnerable at first, so it is important to provide them with a safe and suitable environment. They can be fed a diet of newly hatched brine shrimp or crushed flakes.
Maturity:
The fry of Mexican tetra fish reach maturity within six months. At this point, they are ready to breed and continue the life cycle. It is important to note that Mexican tetra fish can be kept in a community aquarium with other peaceful fish as they are not aggressive.
Behavior
These fish are found in freshwater caves and rivers in Mexico and have evolved to live in complete darkness. As a result, their eyesight has become obsolete, and they rely on their other senses to navigate their environment.
Sense of Smell
One of the most important senses for Mexican blind cave tetra fish is their sense of smell. They use this sense to locate food in their environment. Mexican tetra fish have a keen sense of smell, and they can detect food from a distance. They use their sense of smell to find small invertebrates, algae, and other food sources in their environment.
Lateral Line System
Mexican blind cave tetra fish also use their lateral line system to detect movement and vibrations in the water. This system is a network of sensory cells that are located on the sides of their body. When something moves in the water, it creates a vibration that is detected by the sensory cells in the lateral line system. This allows the fish to detect the movement of predators and prey in their environment.
Heightened Sense of Touch
Mexican tetra fish have also evolved to have a heightened sense of touch. This allows them to detect changes in
their environment and avoid predators. They have sensitive skin and can detect changes in water temperature, pressure, and flow. This helps them to navigate their environment and avoid obstacles.
Behavior in Captivity
In captivity, Mexican tetra fish should be kept in a dimly lit aquarium with plenty of hiding places. They may be shy at first, but will quickly adjust to their environment. It is important to keep the water clean and well-filtered as these fish are sensitive to water quality. Mexican tetra fish are also social creatures and should be kept in groups of at least 5 to 6 fish.
Breeding Behavior
Mexican blind cave tetra fish are egg layers and will breed in captivity. Breeding is triggered by changes in water temperature and the addition of fresh water to the aquarium. The female will lay eggs on a flat surface, and the male will fertilize them. The eggs will hatch in about 4 to 5 days, and the fry will be free-swimming in about a week.
Importance of Mexican Tetra Fish
Mexican tetra fish play an important role in their ecosystem. As a primary consumers, they feed on algae and other small organisms, helping to maintain the balance of the food chain.
They are also a great way to study how animals’ eyes and behaviors have changed over time. They have also become popular in the aquarium trade because of how unique they look and how well they can adapt to different environments.
Like any living creature, these fish are susceptible to a variety of diseases that can affect their health and well-being. It is important to maintain good water quality, avoid overcrowding, and monitor your fish for any signs of illness. If you notice any symptoms of disease, it is important to isolate the affected fish and treat the tank with medication specifically designed to kill the parasite or bacteria causing the infection. Below are the most common diseases:
1. Ich (Ichthyophthirius multifiliis)
Ich is a highly contagious disease caused by a parasite that attaches itself to the fish’s skin and fins, causing small white spots to appear. If left untreated, ich can quickly spread throughout the tank and cause severe damage to the fish’s health. To prevent ich, it is essential to maintain good water quality and avoid overcrowding. If your Mexican tetra fish develop ich, you can treat the tank with medication specifically designed to kill the parasite.
2. Fin Rot (Columnaris)
Fin rot is a bacterial infection that affects the fins and tail of the fish, causing them to appear frayed and ragged. It is often caused by poor water quality, overfeeding, or overcrowding. To treat fin rot, it is important to isolate the affected fish and clean the tank thoroughly. You can also use medication specifically designed to kill the bacteria causing the infection.
3. Dropsy (Edema)
Dropsy is a condition that occurs when there is a buildup of fluid in the fish’s body cavity, causing the abdomen to swell. It is often caused by poor water quality, overfeeding, or bacterial infections. Unfortunately, dropsy is difficult to treat, and many fish do not survive the condition. However, you can try treating the fish with antibiotics and improving the water quality to give them the best chance of recovery.
4. Velvet (Oödinium)
Velvet is a parasitic infection that causes a yellow or gold dusting to appear on the fish’s skin. It is often caused by poor water quality or stress, and can quickly spread throughout the tank. To treat velvet, you can use medication specifically designed to kill the parasite causing the infection, and improve the water quality to prevent further outbreaks.
5. Swim Bladder Disease
Swim bladder disease is a condition that affects the fish’s ability to control their buoyancy, causing them to float to the surface or sink to the bottom of the tank. It is often caused by overfeeding or poor water quality, and can be exacerbated by stress. To treat swim bladder disease, you can try adjusting the fish’s diet and feeding them smaller, more frequent meals. You can also improve the water quality and reduce stress levels in the tank to give them the best chance of recovery.
Mexican Tetra Fish Predators
If you’re a Mexican tetra fish enthusiast, you might be worried about the survival of these beautiful creatures. And indeed, there are several threats that they are facing, including predation by other fish species. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at Mexican tetra fish predators and what you can do to protect your tetras.
Invasive species
One of the biggest threats to Mexican tetra fish populations comes from invasive species. These are non-native species that have been introduced to the ecosystem and compete for resources with the tetras. Invasive species can also prey on the tetras, making it harder for them to survive. Some of the most common invasive species that threaten Mexican tetras include tilapia, catfish, and crayfish.
Habitat loss
Habitat loss and degradation due to urbanization and agriculture are also major threats to Mexican blind cave tetra fish populations. As their natural habitat is destroyed or altered, it becomes harder for the tetras to find food, shelter, and other essential resources. This can lead to a decline in their populations over time.
Pollution
Pollution and changes in water quality can also have negative impacts on the health and behavior of Mexican blind cave tetra fish. Polluted water can make it difficult for the tetras to breathe and can also affect their ability to reproduce. Additionally, changes in water temperature and acidity can have negative impacts on their health and behavior.
Larger fish
Mexican blind cave tetra fish are small and peaceful creatures that can fall prey to larger fish species in the wild. Some of the fish species that are known to prey on Mexican tetras include cichlids, pufferfish, and larger catfish species. If you’re keeping Mexican tetras in an aquarium, it’s important to make sure that they are not housed with larger, aggressive fish that might see them as prey.
Birds
Mexican tetras are also vulnerable to predation by birds that feed on small fish. Some of the bird species that are known to prey on Mexican tetras include kingfishers, herons, and egrets. If you’re keeping Mexican tetras in an outdoor pond, it’s important to make sure that there are adequate hiding places for the tetras to escape from bird predators.
Feeding
Their diet in the wild varies from location to location, but in captivity, they are omnivorous and can thrive on a combination of commercial flakes and live or frozen foods. Here’s what you need to know about feeding your Mexican tetra:
Commercial Foods: Mexican tetras can be fed a high-quality commercial flake food as a staple part of their diet. Look for flake foods that are specifically formulated for omnivorous fish and contain a mix of proteins and plant matter.
Live or Frozen Foods: To supplement their diet, you can offer your Mexican tetra live or frozen foods like brine shrimp, daphnia, bloodworms, and insect larvae. These foods are high in protein and will provide your fish with essential nutrients.
Algae Wafers: Mexican tetras are known to nibble on algae, so adding algae wafers to their diet can be beneficial. Algae wafers are made from dried algae and provide a good source of fiber and essential nutrients.
Vegetables: Although Mexican tetras are primarily carnivorous, they can benefit from some vegetable matter in their diet. You can offer them small amounts of blanched spinach, peas, or cucumber. These vegetables are a good source of fiber and can help keep your fish healthy.
Feeding Frequency: Mexican tetras should be fed small amounts multiple times a day, rather than one large feeding. This will help prevent overfeeding and keep the water quality in your aquarium stable.
Sinking Foods: Mexican tetras are known to be slower than other fish when it comes to getting to their food. Adding sinking pellets or tablets can help ensure that they are getting enough to eat.
Experiment with Food: It’s essential to experiment with different types of food to see what your Mexican tetra prefers. Try offering them a variety of foods and see what they like best. Over time, you’ll learn what their favorite foods are and adjust their diet accordingly.
Avoid Overfeeding: Overfeeding your Mexican tetra can lead to health problems and water quality issues in your aquarium. Be sure to only feed your fish what they can eat in a few minutes, and remove any uneaten food from the tank.
Breeding
Breeding Mexican Tetra Fish can be a rewarding experience for aquarists. This species is easy to breed and can be a great addition to your aquarium. Mexican Tetras are native to Mexico, Belize, and Guatemala, and are known for their beautiful coloration and active behavior. Here are the steps you should take to successfully breed Mexican Tetras in captivity.
Set up a Breeding Tank
The first step in breeding Mexican Tetras is to set up a breeding tank. A 10-gallon tank is sufficient for breeding a pair of Mexican Tetras. Decorate the tank with live plants such as Java Moss, Water Wisteria, and Anacharis to provide hiding places for the fish to lay their eggs. Add a sand or gravel substrate and scatter large marbles all over the substrate. This will prevent the eggs from being eaten by the adults. Fit the breeding tank with a sponge filter to maintain water quality.
Choose a Breeding Pair
Choose a healthy breeding pair of Mexican Tetras. The male is usually more colorful and has longer fins than the female. Make sure the male and female are of similar size and age. Introduce the breeding pair to the breeding tank and let them acclimate for a few days.
Feed High-Protein Foods
Feed the breeding pair high-protein foods such as live or frozen brine shrimp, bloodworms, and daphnia. This will help the fish to develop healthy eggs and sperm. Feed the fish twice a day and remove any uneaten food to maintain water quality.
Observe Spawning Behavior
Mexican Tetras are egg-layers and will spawn by laying eggs on the substrate. The female will lay eggs and the male will fertilize them. The eggs will hatch within 24 hours. Observe the spawning behavior and remove the adults from the tank once the eggs have been laid. This will prevent the adults from eating the eggs or the fry.
Care for the Fry
Once the eggs have hatched, the fry will begin to swim freely. Feed the fry small amounts of infusoria or powdered fish food several times a day. Gradually increase the size of the food as the fry grow. Keep the water clean by performing regular water changes and maintaining good water quality.
If you notice the fish biting each other or flaring their gills, you should immediately cease the breeding process. This behavior indicates that the fish is in discomfort.
Conservation Efforts
Tank Setup
If you are planning to keep Mexican Tetra fish, also known as blind cave tetra, as pets, then you need to set up a suitable aquarium for them. Although a minimum of 20 gallons is recommended for these fish, it is better to have a larger tank if you plan to add other species. Here are some helpful tips to set up a Mexican tetra fish tank:
Decorations:
– Line the bottom of your tank with a dark sand or gravel substrate. This will help bring out the colors of your fish, and also mimic their natural habitat.
– Consider adding a cave or two in which your fish can shelter. This will help them feel safe and secure, especially when they are first introduced to the tank.
– The Mexican tetra will not harm your live plants, so feel free to add any that can tolerate the water conditions. Plants like Java fern, Anubias, and Amazon swords are great choices.
Water Conditions:
– Mexican tetras like consistently warm waters in the temperature range of 68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit (20 to 25 degrees C). You can use a heater and thermometer to maintain the water temperature within this range.
– The pH level should be between 6.8 and 8.0, and the hardness between 90 to 447 ppm. You can use a water testing kit to monitor these levels and adjust them accordingly.
Equipment:
– Use a filter with a flow rate of four to five times the volume of your tank. This will help maintain good water quality and oxygenation. You can choose from different types of filters such as sponge filters, hang-on-back filters, or canister filters.
– A good lighting system is also important for your plants to thrive. You can use LED lights that are designed specifically for planted aquariums.
– It is also a good idea to have a substrate vacuum and algae scraper on hand to help with cleaning and maintenance.
Τank Mates
If you’re looking to add some Mexican tetras to your aquarium, it’s important to carefully consider their tank mates. Mexican tetras are peaceful fish that enjoy swimming in the middle of the tank, so it’s best to choose tank mates that occupy the top or bottom of the tank. Here are some great options for Mexican tetra tank mates:
Barbs: Barbs are active fish that enjoy swimming near the top of the tank. They come in a variety of colors and are known for their playful personalities. Some good options for tank mates include cherry barbs, gold barbs, and rosy barbs.
Gouramis: Gouramis are another great option for Mexican tetra tank mates. They come in a variety of sizes and colors, and are known for their peaceful nature. Some good options include dwarf gouramis, pearl gouramis, and honey gouramis.
Other tetra fish: Mexican tetras are part of the tetra family, so it’s no surprise that other tetra fish make great tank mates. Some good options include neon tetras, cardinal tetras, and glowlight tetras.
Corydoras catfish: These bottom-dwelling fish aregreat companions for Mexican tetras because they keep to themselves and won’t bother the tetras. Corydoras catfish are also known for their scavenging abilities, which help keep the tank clean. Some good options include bronze corydoras, peppered corydoras, and panda corydoras.
Plecos: Plecos are another great option for bottom-dwelling tank mates. They are known for their algae-eating abilities and can help keep your tank clean. Some good options include common plecos, bristlenose plecos, and rubber lip plecos.
It’s important to note that Mexican tetras are not suitable for a community tank that includes non-fish tank mates such as snails, shrimps, and other crustaceans. Mexican tetras are known to nibble on and bite non-fish tank mates, which can cause harm or stress to those creatures. It’s best to keep snails and shrimps in a separate tank if you want to keep them as pets.
What is the Price Range of Mexican Tetra Fish?
The price range of Mexican blind cave tetra fish can vary depending on where you purchase them from. Here are some general price ranges that you can expect:
– Pet stores: Mexican Tetra fish can typically be found at pet stores for anywhere between $1 and $5 per fish. The price may vary depending on the size and quality of the fish, as well as the location of the pet store.
– Online retailers: You can also purchase Mexican Tetra fish from online retailers. The price may be slightly higher than what you would pay at a pet store, but you will have a wider selection to choose from. Mexican Tetra fish can typically be found online for anywhere between $3 and $10 per fish, depending on the retailer.
– Specialty breeders: If you are looking for high-quality Mexican Tetra fish, you may want to consider purchasing from a specialty breeder. These breeders focus on breeding high-quality fish with desirable traits, such as unique coloration or larger size. Prices for Mexican Tetra fish from specialty breeders can range from $10 to $50 per fish or more.
There are several factors that can influence the price of Mexican Tetra fish, including:
– Size: The size of the fish can impact the price. Smaller fish are generally less expensive than larger fish, as they require less food and space.
– Quality: High-quality Mexican Tetra fish with desirable traits, such as unique coloration or larger size, may be more expensive than average fish.
– Breeder: Mexican Tetra fish from specialty breeders may be more expensive than those from pet stores or online retailers, as they are typically bred for specific traits.
– Location: The cost of Mexican Tetra fish can vary depending on where you live. In areas where the fish are more rare or difficult to obtain, they may be more expensive.
It is important to note that the cost of Mexican Tetra fish is not the only factor to consider when purchasing them for your aquarium. You should also consider the cost of the aquarium itself, as well as other equipment such as filters, heaters, and lighting. Additionally, you will need to factor in the cost of food and other supplies, as well as ongoing maintenance costs.
Do Mexican Tetra Fish Scream?
One question that has been asked is whether or not Mexican tetra fish scream.
To answer this question, it is important to understand what screaming is and why animals do it. Screaming is a vocalization that animals use to communicate distress, fear, or pain.
It is typically a high-pitched sound that is meant to attract attention and signal for help.
Many animals, including humans, use screaming as a survival mechanism to alert others to danger or to communicate their needs.
In the case of Mexican tetra fish, there is no evidence to suggest that they scream in the same way that mammals or birds do.
Fish do not have vocal cords like mammals do, and therefore cannot produce the same range of sounds. However, fish do have other ways of communicating with each other, such as through body language and chemical signals.
While Mexican tetra fish may not scream in the traditional sense, they do have unique adaptations for living in their cave environments. For example, they have lost their eyes and pigmentation due to living in complete darkness for generations. This has led to the development of other sensory organs, such as their lateral line system, which allows them to sense vibrations and movements in the water.
They also have enhanced sense of smell, which they use to navigate and find food.
Despite their lack of vocalizations, Mexican tetra fish are fascinating creatures to observe in an aquarium setting.
They are active and curious fish that can live up to 10 years in captivity. They are omnivores and will eat a variety of foods, including flakes, pellets, and live or frozen foods such as brine shrimp or bloodworms.
They do well in groups and should be kept in a tank that is at least 20 gallons, with plenty of hiding places and plants to mimic their natural environment.
Are Mexican Tetra Fish Suitable for Beginner Aquarists?
If you’re a beginner aquarist looking for an easy-to-care-for fish, the Mexican tetra fish might be a great option for you. Here’s why:
1. Hardy fish
Mexican tetras are a hardy fish species that can adapt to different water conditions, making them suitable for beginner aquarists. They can tolerate a wide range of temperatures, pH levels, and water hardness. This means that even if you make mistakes in maintaining the water conditions, they will still thrive.
2. Easy to feed
Mexican tetra fish are omnivores, which means they eat both plant and animal-based food. They will eat almost anything you feed them, including flakes, pellets, and live or frozen food. This makes feeding them easy and straightforward.
3. Peaceful fish
Mexican tetra fish are peaceful and can be kept in a community tank with other peaceful fish species. They are not aggressive, so they won’t bother other fish in the tank. However, it’s important to note that they may nip the fins of long-finned fish.
4. Beautiful fish
Mexican tetra fish are also known for their beauty. They have a striking silver color with a black stripe that runs from their eyes to their tails. They also have a red-orange spot on their tails, making them visually appealing in any aquarium.
5. Easy to breed
Breeding Mexican tetra fish is relatively easy. They are egg-layers, which means they lay their eggs on a substrate or plant. The eggs will hatch within a few days, and the fry will become free-swimming after a week. This makes them a great option for aquarists who want to try breeding fish for the first time.
6. Low-maintenance fish
Mexican tetra fish are low-maintenance fish that don’t require a lot of attention or special care. They don’t need a lot of space, so they can be kept in smaller tanks. They also don’t produce a lot of waste, so you don’t need to change the water as frequently as with other fish species.
How do Mexican Tetra Fish Find Food in the Dark?
Mexican tetra fish have developed some impressive survival skills that have helped them navigate their dark aquatic environment.
They rely on their sense of smell and their lateral line system to locate prey, which allows them to feed and mate.
One of the key adaptations that has helped these fish to feed is the development of large jaws, additional teeth, and an increased number of tastebuds around their mouth and head.
This combination of features enables them to identify and consume a wide range of prey items.
In addition to their impressive feeding abilities, Mexican tetra fish also have an incredible memory that helps them to navigate their habitat.
They can map out their surroundings and use feedback from their lateral lines to get around, even in complete darkness.
This sensory system allows them to detect vibrations in the water and determine the location of nearby objects, such as predators or potential mates.
Conclusion
The Blind Mexican Tetra Cave is a fascinating ecosystem that is worth studying and exploring.
The unique features of the cave, such as its total darkness and lack of predators, have led to the evolution of a unique species of fish that is completely blind.
Mexican Tetra Cave serves as a reminder of the incredible adaptability of life and the importance of preserving our planet’s natural wonders.
Understanding these organisms and their habitats can give us a better insight into the complexities of nature and the need for conservation efforts to maintain these fragile ecosystems.